We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Detailed information

Select a Country

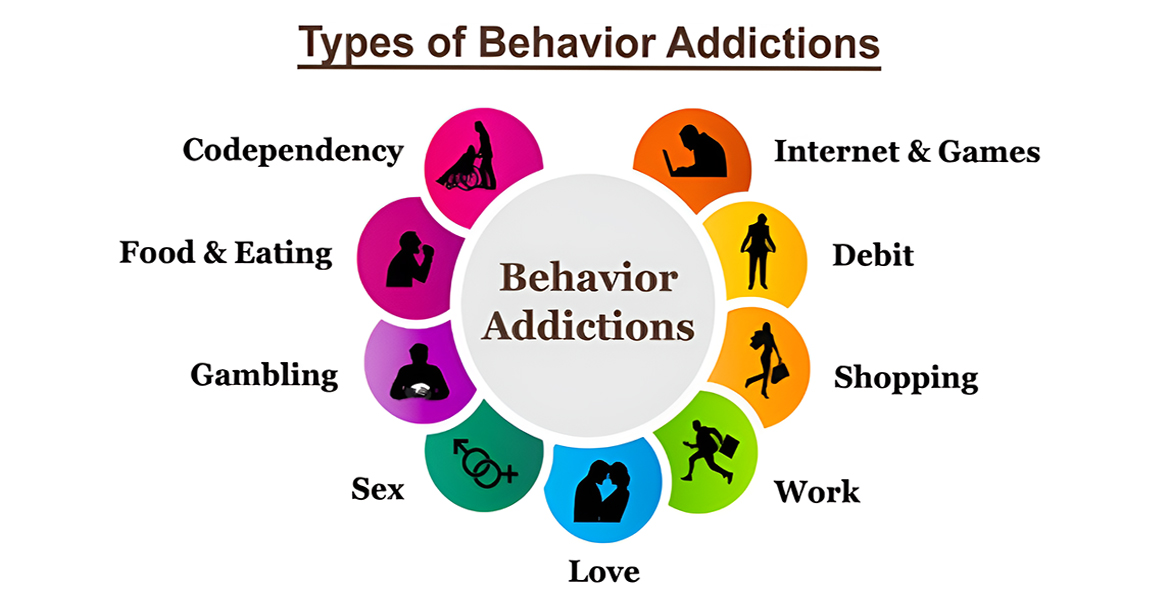
The term behavioral addiction refers to an individual developing an intense attraction or compulsive inclination towards a specific behavior. These types of addictions arise when certain behaviors trigger the brain's reward and pleasure mechanism through repetition.
Addictions are typically divided into two primary categories: behavioral and chemical. Behavioral addictions represent situations where individuals experience discomfort, but the condition does not stem from substance use; instead, it revolves around specific behaviors. In such cases, individuals may find pleasure, relaxation and a sense of well-being when engaging in certain behaviors. However, if these behaviors lead to adverse outcomes, individuals may lose control over them, experience a weakened willpower and become mentally and physically consumed, indicating a behavioral addiction.

Individuals with addiction often find their behaviors psychologically satisfying or enjoyable. However, feelings of guilt, remorse or anger may follow, leaving them feeling helpless due to the consequences of their ongoing choices. Coping with behavioral addictions can be challenging, as individuals often struggle to quit or reduce a specific behavior or action without treatment or intervention, leading to unsuccessful attempts to quit.
Numerous studies in the literature highlight the distinction between investigating the action that triggers addiction and its pathological level of use, compared to chemical addictions. While chemical addictions are characterized by tolerance and withdrawal, these physical symptoms may not be as evident in behavioral addictions. However, they still manifest to some extent. For a behavior to be considered addictive, it must encompass criteria such as mental preoccupation, mood variability, tolerance, withdrawal, interpersonal conflict and repetition.
 References
References
For more detailed information on the topics covered in this section, you may refer to the following sources:
- Grant, J. E. (2010). Introduction to Behavioral Addictions. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 36(5), 233–241.
- Murphy, E. (2023, May 26). Behavioral Addictions.
- Turkish Green Crescent Society
To answer your questions in the fields of Addiction and Public Health...

All rights are reserved 2026 © International Federation of Green Cresent
Personal Data Protection Policy
Terms and Conditions
Copyright 2026 © International Federation of Green Cresent